How Do Coconuts Collect Water Inside? Unveiled Nature’s Process!

Ever cracked open a coconut and wondered, “How on earth did this tropical delight get filled with such refreshing water?” It’s like nature’s own mystery box! Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the fascinating process behind the coconut’s internal reservoir.
The Coconut Palm: Nature’s Ingenious Engineer
The coconut palm (Cocos nucifera) is a marvel of nature, thriving in sandy soils and coastal areas where other plants might struggle. Its secret weapon? A fibrous root system designed for efficiency. Unlike trees with a single taproot, the coconut palm boasts a network of thin roots that spread out near the soil’s surface, ready to absorb water and nutrients. citeturn0search17
From Soil to Sky: The Journey of Water
- Absorption: The adventure begins in the soil. The coconut palm’s roots draw in water through a process called osmosis. Think of it as the tree’s way of sipping water, moving it from areas of low concentration in the soil to higher concentrations within the root cells.
- Transportation: Once inside the roots, the water embarks on an upward journey through specialized tissues known as xylem. These act like the tree’s plumbing system, channeling water up the trunk to various parts, including the developing coconuts.
- Filtration: As the water ascends, the tree employs a natural filtration system, removing impurities and excess salts. By the time it reaches the coconut, the water is a nutrient-rich, hydrating liquid.
Inside the Coconut: The Magic Unfolds
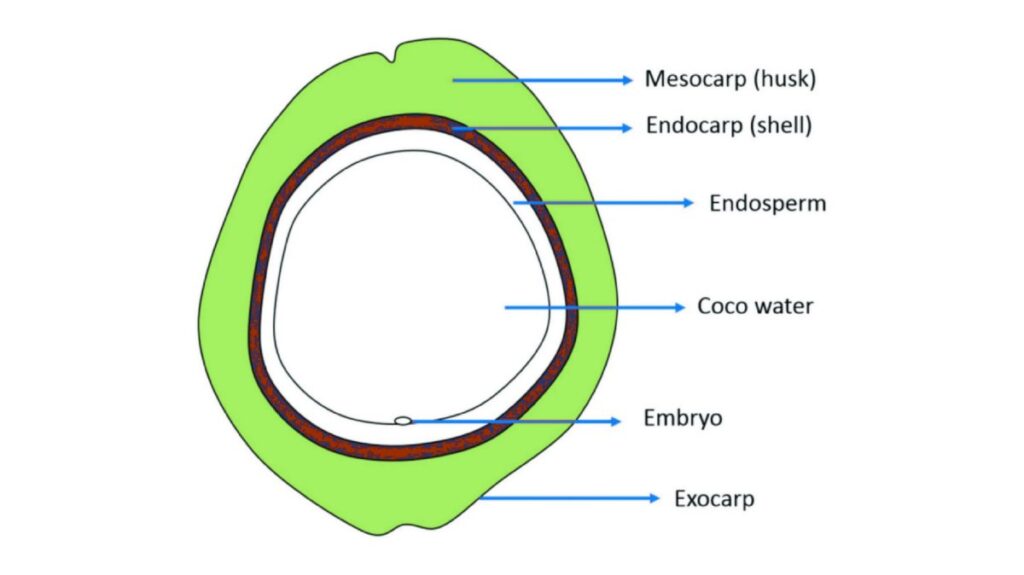
Within the young, green coconut, the water serves a vital role. Initially, it’s a suspension medium for the endosperm during its nuclear phase. As the coconut matures, this liquid endosperm begins to deposit onto the inner walls, gradually forming the solid “meat” or flesh we enjoy.
Why Store Water? The Coconut’s Survival Strategy
You might wonder, “Why does a coconut need to store water?” It’s all about survival and propagation. The water-rich endosperm provides essential nutrients to the developing seed. When a coconut falls and finds itself in a conducive environment, this internal reservoir supports the seedling until it establishes its own root system. It’s like a built-in survival kit!
A Sip of Science: The Composition of Coconut Water
Beyond quenching our thirst, coconut water is a cocktail of beneficial compounds:
- Electrolytes: Packed with potassium, magnesium, and calcium, it’s nature’s sports drink, helping to replenish essential minerals.
- Phytohormones: These natural plant hormones, such as cytokinins, have garnered attention for their potential anti-aging and anti-carcinogenic properties.
- Amino Acids: Building blocks of proteins, aiding in various bodily functions.
From Tree to Table: Harvesting the Elixir
In tropical regions, harvesting coconuts is both an art and a tradition. Young coconuts, typically around 6-7 months old, are prized for their abundant and sweet water content. As the coconut matures, the water gradually converts into the solid endosperm, reducing the liquid volume but enriching the flesh.
Fun Fact: The Versatility of Coconut Water
Did you know that during World War II, in emergency situations, coconut water was used as a short-term intravenous hydration fluid? Its sterile nature and electrolyte balance made it a temporary substitute when medical saline was unavailable. Talk about a multi-purpose drink!
Cracking the Mystery

So, the next time you enjoy the refreshing taste of coconut water, you’ll appreciate the intricate natural processes that filled that coconut. From the soil’s embrace to the tree’s filtration finesse, it’s a testament to nature’s ingenuity. Cheers to that!
You would have ever thought: How Can Someone Forget Everything But Still Remember Their Mother Tongue? The Science Behind This!